CockroachDB is a distributed SQL database that aims to make it simple to build, deploy, and operate globally-scaled applications. It is designed to be highly available, survive data center outages, and maintain consistent performance across a geographically distributed database cluster.
One of the key features of CockroachDB is its ability to automatically shard data across multiple nodes in a cluster, allowing it to scale horizontally as more nodes are added.
This pattern provides a Terraform Module that can be used to deploy CRDB multi node database cluster in a single EKS cluster using CockroachDB Kubernetes Operator. It his also uses cert-manager to secure node communication with TLS certificate.
About this Repo
This repo provides a Terraform Module that can be used to deploy CRDB multi node database cluster in a single EKS cluster using CockroachDB Kubernetes Operator. It his also uses cert-manager to secure node communication with TLS certificate.
Requirements
- An active AWS account with required permission to deploy resources in Kubernetes cluster
- A running EKS cluster with version v1.23+ , EKS Node should have kubernets label
node=cockroachdb - EBS CSI Driver v1.19.0+ installed in the EKS cluster
- An Understanding of Terraform and usage.
- Terraform CLI with version 1.0.0+
- Install Kubectl
- AWS CLI v2.9.18+
- A web browser that is supported for use with the AWS Management Console. (See the list of supported browsers)
Target Architecture
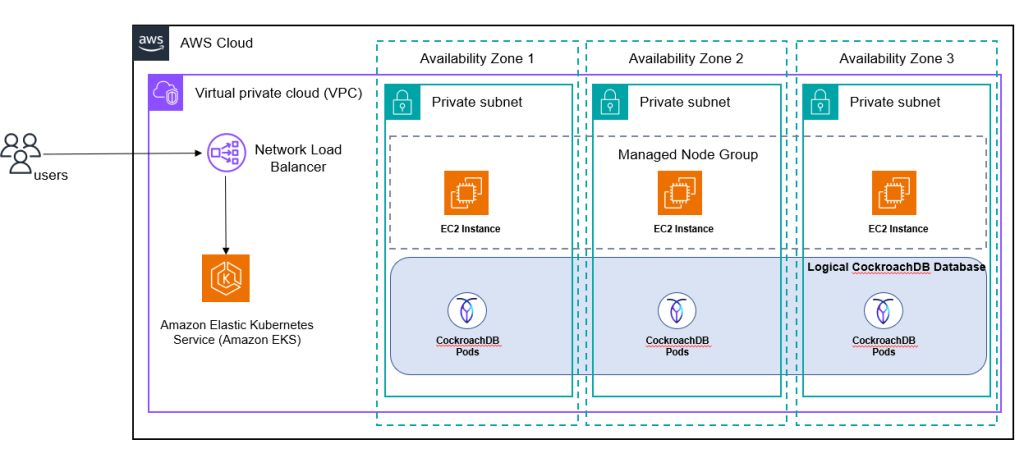
How to install
Setup
- git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/crdb-cluster-eks-terraform.git
- Update variable.tf under main folder to the required value. For more information on all variables, refer to the README file inside
modules/crdbfolder.
Install
- terraform init
- terraform apply
Verification
- Verify if kubectl is installed. Follow instructions to install kubectl
kubectl version- Set the eks context using aws cli
aws eks update-kubeconfig --name <eks_cluster_name> --region <AWS_Region_Name>- Verify number of CRDB pods using
kubectl get pods -n <namespace>
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cockroach-operator-655fbf7847-zn9v8 1/1 Running 0 30m
cockroachdb-0 1/1 Running 0 24m
cockroachdb-1 1/1 Running 0 24m
cockroachdb-2 1/1 Running 0 24m- 3 cockroach dB pods will be running as the default value in the variable.tf is set to 3. This may vary based on the value set on variable.tf file.
Scale up/down:
- Increase/decrease the number of nodes for managed node group in ./main/variable.tf and perform
terraform apply
Note – Due to POD anti-affinity rule, only one CRDB Pod can run in one EKS worker note. Hence,use EKS autoscaler or Karpenter for autoscaling worker nodes automcatically to run the additional CRDB nodes (POD)
- For example, if number of nodes is increased from 3 to 4, you would see 4 pods are running after executing
terraform apply
kubectl get pods -n <namespace>NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
cockroach-operator-655fbf7847-zn9v8 1/1 Running 0 30m
cockroachdb-0 1/1 Running 0 24m
cockroachdb-1 1/1 Running 0 24m
cockroachdb-2 1/1 Running 0 24m
cockroachdb-3 1/1 Running 0 30s
Clean Up
To tear down, run
terraform destroyTroubleshooting
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Error validating provider credentials | When you run the Terraform apply or destroy command from your local machine, you might encounter an error similar to the following: Error: configuring Terraform AWS Provider: error validating provider credentials: error calling sts:GetCallerIdentity: operation error STS: GetCallerIdentity, https response error StatusCode: 403, RequestID: 123456a9-fbc1-40ed-b8d8-513d0133ba7f, api error InvalidClientTokenId: The security token included in the request is invalid.This error is caused by the expiration of the security token for the credentials used in your local machine’s configuration.To resolve the error, see Set and view configuration settings in the AWS CLI documentation. |
| CRDB nodes ( PODs) in pending state | 1. Due to POD podAntiAffinity Rule, only one CRDB pod can be schedule in one EKS node. If number of CRDB node exceeds number of EKS nodes available, then CRDB nodes ( PODs) might be in pending state. In that case, you need to implement Cluster Autoscaler or Karpenter so that EKS node scales automatically. Visit this page, for more details. 2. Check if Kubernetes worker nodes has correct label node=cockroachdb with the command kubectl get nodes --show-labels . If not, you need to make sure all the worker nodes ( current and future) gets the above label for CRDB PODs to be scheduled |
Related Resources
- EKS Getting started
- Installing Kubectl
- Install CRDB on single cluster
- Install CRDB on multi cluster
- Terraform installation guide
- Terraform remote state management
- Terraform AWS Provider – Documentation and Usage
- EKS setup
Additional information
- Prerequisites creating EKS cluster
- Terraform binary download
- Install Terraform
- If you stop Kubernetes without first deleting the persistent volumes, they will still exist in your cloud project.
- delete crdb –
eksctl delete cluster --name cockroachdb
Credits: Sandip Gangapadhyay, Co-Author, AWS
